Previous Story
Proof of Work is a consensus algorithm that enables the network to agree on the order of transactions and blocks. In other words, it’s a way to make sure that all nodes (computers on the network) agree with one another. Instead, it used a proof of stake system, which required participants to have some amount of bitcoin for them to be able to participate in mining or staking.
In a proof-of-work system, the first node to solve a given problem receives a reward for its effort. This means that if you have a computer that has access to resources like electricity and storage space, you can use that resource to mine cryptocurrency. In this article, you will learn details about proof of work.
Proof of work is a concept in computer science and cryptography whereby a piece of data must be difficult (or impossible) to produce without the consent of the person or entity using the data. The proof of work prevents users from creating alternative chains and thus gaining control over the system. The blockchain incorporates a public ledger that records transactions on a digital ledger, but unlike a traditional database, it uses cryptography to ensure data integrity and prevents tampering with information.
Proof of work is a consensus algorithm that allows the network to agree on the validity of transactions. For a transaction in the blockchain, it must be validated by the network. This can be done using several different ways. Proof of Work (PoW) is the first and most popular method. In this method, miners compete with each other to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions. If a miner solves these problems quickly enough, they will be rewarded with newly created Bitcoins and added to the blockchain.
Thrashing is another way in which you can help validate transactions on the Bitcoin network. It involves running your computer fully but not doing anything useful (for example, downloading large files or playing games). Running thrash cycles helps ensure that all blocks are mined before they can be filled with data as part of a block reward or transaction fee payment. Proof of Stake (PoS) is another consensus algorithm that has gained popularity over time. Rather than mining blocks and validating transactions, users stake their coins to gain rewards from participating in the network’s consensus process.
The innovation of Proof of Work, proposed by Markus Jakobsson and Ari Juels in 1999, has been one of the most critical developments in cryptocurrency. It is a new way to verify transactions in a distributed network. The original idea was to create a system that would be implemented on top of existing P2P networks. Markus Jakobsson and Ari Juels, in 1999, used a combination of hashing and proof-of-work to achieve a distributed consensus among nodes about the order of transactions. The scheme was called “Proof-of-Work” (PoW).
It started with the idea that a transaction verification process should be as decentralized as possible. This means that every participant should be able to verify transactions efficiently without having access to any centralized database.
The concept was later refined and implemented on top of the Bitcoin network, where it became known as block mining. The PoW scheme is called Proof-of-Work because Bitcoin miners need to solve an expensive mathematical puzzle before adding the transaction to the blockchain and earning themselves a reward. The puzzle is designed to take a large amount of computational power to solve, making it hard for a single entity to control the network’s mining process. This prevents one entity from gaining a majority over the hashing power and censoring transactions.
The system is also designed so that blocks cannot be added until they are signed by many users, preventing one entity from gaining too much control over the system. The original idea behind the proof of work scheme was to provide a way for miners to avoid centralization. The proof of work scheme is designed such that any miner can generate a block, but only the first miner to solve the problem gets a reward. This system creates a computational requirement for new blocks, called the proof of work, or PoW.
The problem is challenging because it requires programmable computers with large amounts of memory to run through all possible input combinations until one finds the correct answer. The first person who can solve this algorithm gets rewarded for their efforts and enters a lottery where they can claim some coins as payment. The more computing power you have at your disposal, your chances of winning the lottery are higher!
The purpose of proof of work (POW) is to achieve consensus in a distributed system. Consensus is the state where all participants agree on a single value. In a system with POW, if one party does not agree with the majority, it will not be able to reach a consensus and, therefore, cannot reach a consensus on the value being verified. This prevents the problem of one person having a majority hash, which would allow them to block other nodes from reaching consensus.
The idea is that the miner who solves a block first gets to add it to the blockchain and get paid some reward for doing so, but if multiple miners are trying to solve blocks at the same time, then one of them will win and be able to create another block on top of theirs (and claim their reward). This problem can be solved by forcing all miners to compete with each other for each new block created, which requires solving a complicated math problem with high levels of randomness involved.
All nodes on the network must validate the block before it is added to the chain; this ensures no one person controls more than 51% of hashing power on any given network and that no group or entity has centralized control over the network or can manipulate it for their benefit (note: Bitcoin uses Proof-of-Work instead of Proof-of-Stake).
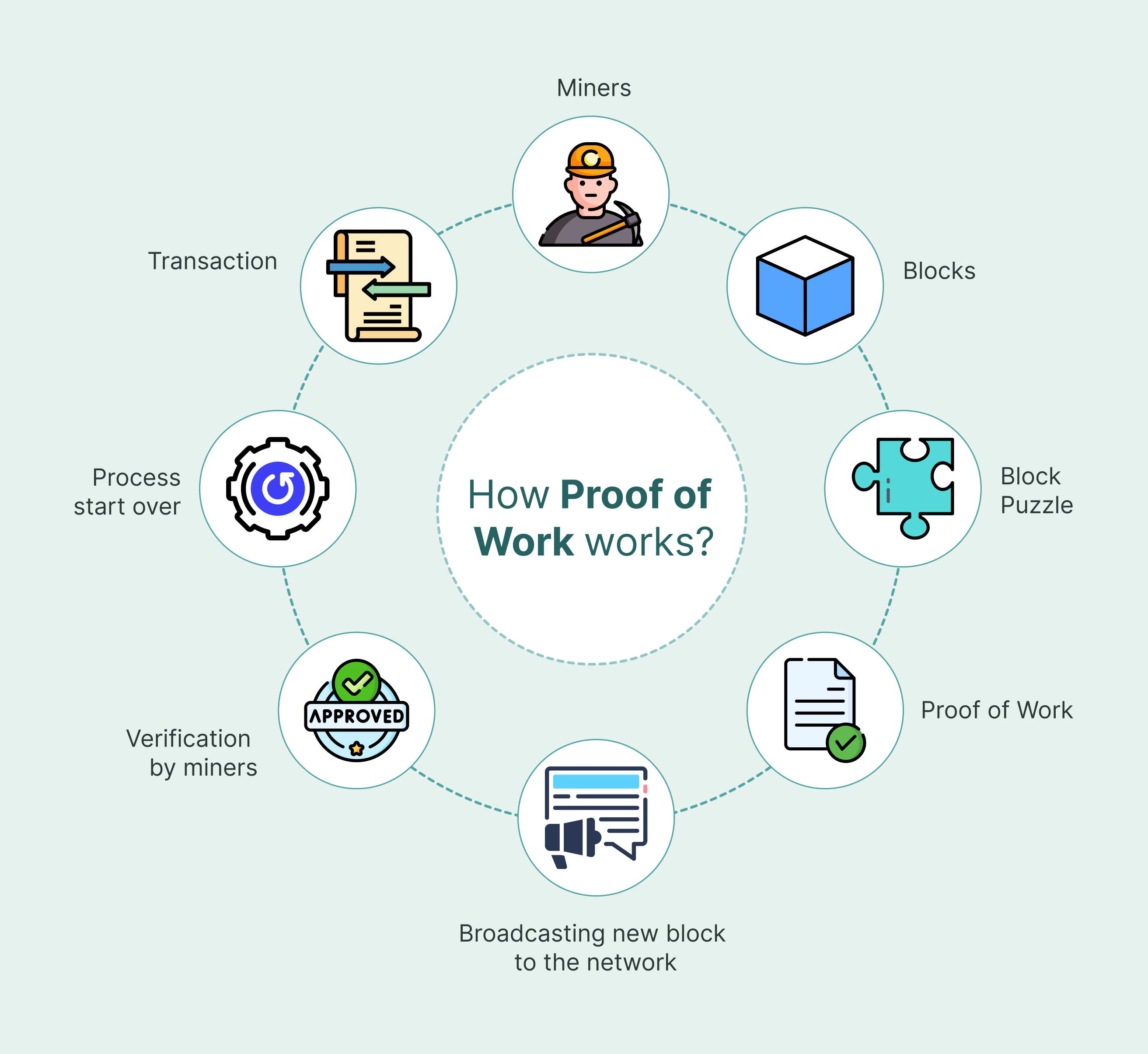
The mechanism of Proof of Work (PoW) is an essential topic in the world of cryptocurrencies. The concept of PoW is that a computer has to expend work to validate a block. This validation process is performed by solving a problem requiring computers to solve math problems.
The problem is called the hash function, which takes user input and outputs many numbers. Other computers on the network verify the output. This verification process is known as mining, and it takes place when users choose to mine for cryptocurrency or participate in the network.
The idea behind POW was that miners would be incentivized to verify blocks because they’d receive new coins. However, this hasn’t happened because no incentives haven’t been built into Bitcoin’s design. In simple terms, miners solve complex mathematical problems called ‘blocks’ to add them to the blockchain. When they solve these blocks, they are rewarded with new bitcoins. This is done through POW mining.
Now that there are millions of transactions every minute, miners have become more specialized than ever, with only large mining pools providing security against 51% of attacks on the network. Proof of Work (PoW) is a distributed consensus algorithm that makes it difficult to fake or reverse engineer the history of a transaction. It also makes it expensive to attack the network.
Proof of work is a consensus algorithm used in cryptocurrencies to verify the legitimacy of an arbitrary number of transactions. It works by having a vast network of participants (miners) do work to find an inappropriate number (hence “proof”) for a block of transactions called a nonce. The miner who solves the proof receives a reward in the form of cryptocurrency.
The primary purpose of proof of work is to ensure that no one can cheat the system by making any extra blocks. This prevents double spending by allowing only one piece of data per block. The secondary purpose is also to ensure that anyone attempting to hack the system cannot simply rewrite all past blocks as new ones since they would not receive any reward for doing so.
The mechanism behind proof of work takes advantage of what is known as “hashing functions”, where given some input, it returns an output with some fixed length and structure. In this way, it is easy to check if two pieces of data are equal (and therefore not an accident) but hard to modify them without changing their hash value or breaking the system entirely.
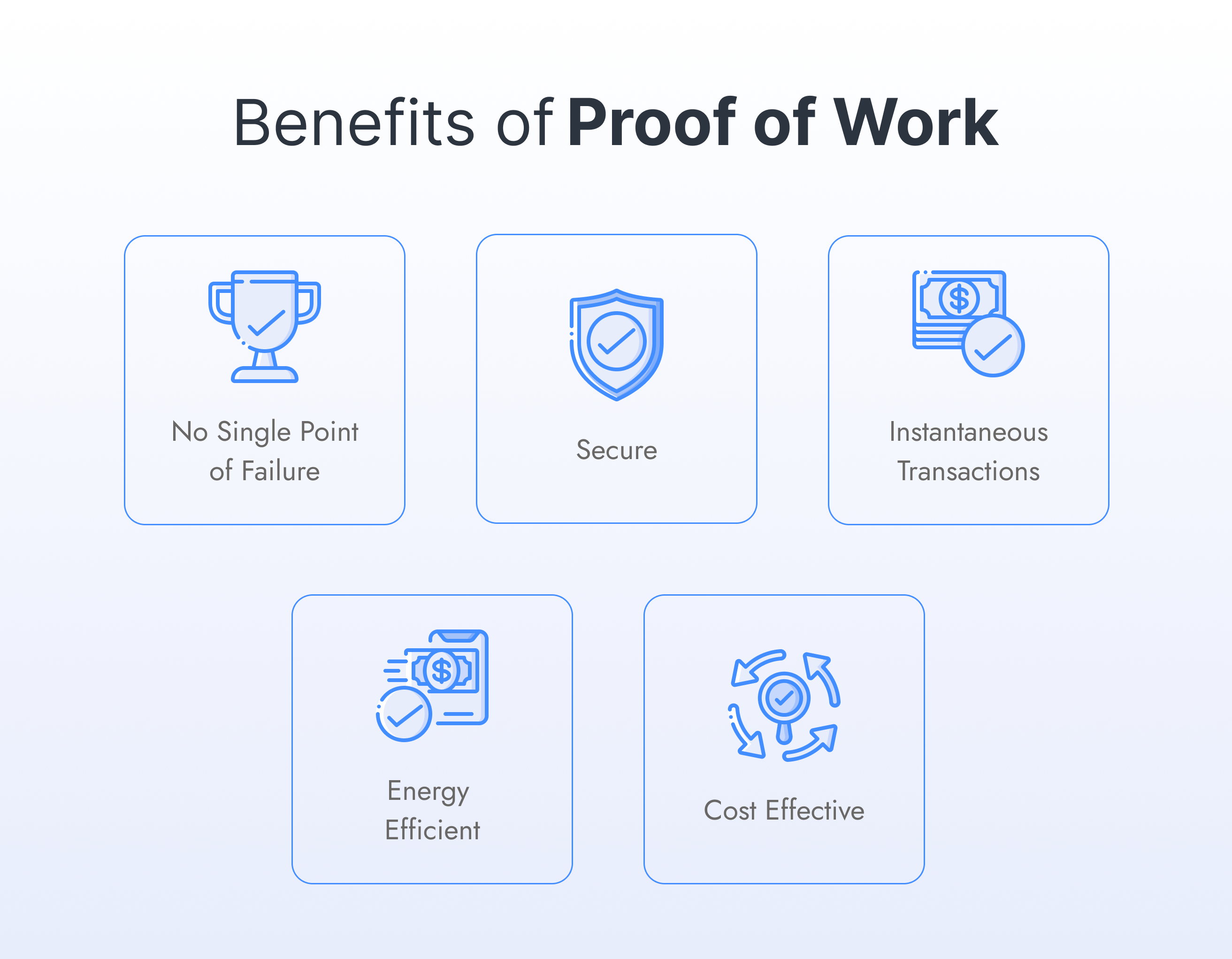
Proof of Work(POW) is a consensus algorithm requiring participants to solve a computationally-intensive problem before they are allowed to participate in the network. This ensures that only participants with real computational power can participate and make decisions. The benefits of Proof of Work(POW) include the following:
The main benefit of POW is that it is not vulnerable to any single point of failure. This means that the system cannot be hacked or attacked by any individual, group, or entity. The security of each node in the network is guaranteed by the work done by all other nodes. There is no need for any central authority to manage and maintain the system. POW is a decentralized mining system, which means that if one machine goes offline, the network will still be able to process transactions. This is unlike other Proof-of-Stake (PoS) cryptocurrencies, where the network would stop working if one node went offline.
The most crucial benefit of POW is that it allows you to build a system that works even if one or more computers fail. For example, the new computer can still run if one computer crashes and another takes over. This means that a blockchain is not vulnerable to a single point of failure like traditional databases are.
The main advantage of Proof of Work(POW) is that it offers complete security and privacy protection to users from various threats such as hacking, theft, or data loss. A hash algorithm has been used for generating blocks and verifying transactions on a blockchain network. In other words, users can send bitcoins without worrying about getting them stolen or lost forever. The miners who validate transactions on the blockchain are the only ones who get rewarded with new coins.
Since they can’t cheat or steal your coins, you are safe from hackers who might try to steal your coins by hacking through your wallet software or exploiting bugs in your CPU/GPU. A blockchain has no central server that can be hacked and taken down. This makes it much more secure than databases because there is no central point where all information is stored. If someone hacks into the database server, they still have access to all data stored on it as long as they don’t delete any files or corrupt them somehow. With a blockchain, if someone hacks into one node, they won’t be able to access information from anywhere else connected to it.
The main benefit of Proof of Work(POW) is that it allows instant transactions between parties without requiring third parties like banks or governments to facilitate such transactions. Users can directly transfer money from one party to another without involving any third party. Another benefit of using POW instead of SQLite (or some other database) is that transactions are processed instantaneously. This means that you don’t need to wait for your transaction to go through before doing anything else, and it also allows you to process transactions faster because they’re not waiting on each other. It does not require anyone to trust any centralized entity with their money or information. It also provides instant transactions instead of waiting days for confirmation before spending your funds.
Blockchains are energy efficient because they use a proof-of-work (POW) mechanism to validate transactions. This mechanism requires miners to expend computing power for the Proof of Work (PoW) algorithm, which is why Bitcoin and Ethereum have such high fees. POW is also known as “mining.” PoW is energy efficient because it does not require any special hardware and does not need special software. It runs on many computers at the same time. It is more decentralized than other consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Authority (PoA).
In PoW, miners compete with each other to solve complicated mathematical problems. The first miner to solve it gets rewarded with the block reward and transaction fees from the new block. This incentivizes miners to expend more computing power on the network, making it more secure for users. It is cost-effective because you can use your computer’s processing power to solve problems instead of buying expensive hardware or renting servers from third parties. You can also use your idle computer’s resources to mine cryptocurrencies without paying electricity bills or renting servers from third parties.
The idea behind proof of work is that miners compete against each other to solve complex math problems, add new blocks to the blockchain network, and receive bitcoins as payment or rewards for their efforts. Proof of work and blockchain are different things. Blockchain is the underlying technology for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin. Proof of work is a system that aims to ensure that the community verifies blocks of data in a distributed ledger system.
There are multiple ways to carry out the proof-of-work mining process. Still, they all involve solving a mathematical problem that anyone can verify using computers or smartphones running specialized software called miners. Proof of work (PoW) is a method for securing a cryptocurrency network and achieving distributed consensus by requesting users to produce computational results. The most common use of PoW is to protect the integrity of the blockchain, but it can also be used to create digital currencies.
To do this, miners solve complex mathematical puzzles that are difficult to solve by ordinary users. They are rewarded with new coins for their work. The first miner to solve the puzzle receives newly created coins; everyone else who participated in the process also gets a share of those coins. This method has been used in Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies since they were created.
Proof of Work systems requires users to spend computational power on solving complex mathematical problems to create new blocks on a blockchain network. This is done by miners who verify transactions and create new blocks on the blockchain network. The verification process involves solving an algorithm that combines previous block hashes with the block header hash, where one hash must match another before it can be added to the chain.
The Proof of Work (PoW) algorithm is a consensus mechanism that depends on the expenditure of computing power to produce a result. This is in contrast to the Proof of Stake (PoS) protocol which depends on the possession of tokens. It is used to show how Proof of Work can be used as an incentive mechanism for miners to ensure that all nodes maintain finality and reach a consensus on the state of a blockchain network. Proof of work algorithms is used in cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin. They weren’t initially designed for this purpose, however. The original idea behind proof of work was to stop miners from colluding to mine blocks faster than everyone else using a single computer.
© 2025 by Speed1 INC.