Previous Story
Blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions across an extensive network of computers without the need for a central authority. It’s used in cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Ripple. Blockchain is a decentralized ledger that records transactions between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way.
The blockchain records transactions across all computers on the network. Each new block added to this chain contains more information than the previous one and links back to the last block. This makes it almost impossible to change the ledger. In this article, you will learn details about blockchain.
Blockchain technology is the underlying mechanism of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. The block is the essential component of blockchain technology, a collection of data that can be added to the chain one after another. Each block contains a hash pointer pointing to the chain’s previous block.
The second component of blockchain technology is mining, a process where individuals or companies compete to solve mathematical puzzles to create new blocks and add them to the chain. These miners are rewarded with newly created bitcoins for their efforts. Blockchain technology is a digital ledger that records transactions across many computers so that the record cannot be altered retroactively. The blockchain database is maintained by a peer-to-peer network which makes it resistant to cyberattacks and ensures complete transparency.
Blockchain technology uses cryptography to ensure the security of transactions, while each block in the chain contains information regarding the previous block, including hashes of all prior blocks. This allows for the verification of transactions without having to involve a third party. Blockchain technology is the underlying technology that powers cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin. However, blockchain has many other applications, even outside the finance world.
Blockchain was initially developed for the digital currency bitcoin to enable peer-to-peer transactions without needing a trusted third party. But it has since been adopted by many other industries, including supply chain management, healthcare, and government services. The basic concept behind blockchain technology is that it provides a shared distributed ledger that records all transactions on any network in real-time. This means that all parties can see every transaction that comes through the network at any time.
In this way, blockchain serves as a digital record of all transactions on any network. The advantage here is that there is no need for a third party like a bank or certificate authority to verify the legitimacy or accuracy of each transaction. Instead, everyone on the network can check their copy of the record at any time and agree on which records are valid and which aren’t.
Satoshi Nakamoto invented Blockchain, an anonymous person or group who created Bitcoin in October 2008 and was first implemented in 2009. The technology has since been adopted by many industries, including banking and insurance. Blockchain is a new database that can share information across several computers without needing a centralized authority. This is done by using cryptography to ensure the integrity of data and its transmission, making it impossible to change or delete.
Blockchain technology allows parties to transact with each other without relying on a trusted third party. This means there is no need for an intermediary like a bank or government agency when transferring money or exchanging goods and services. Each transaction is recorded as a block on the chain, becoming part of the permanent record stored in the ledger. It is a distributed database where all the transactions are recorded into blocks and then added to the chain. It is like an open-source bookkeeping system that prevents fraudulent activities and ensures transparency for everyone involved.
The main advantage of this technology is that it allows users to share information without relying on third parties such as banks or governments. This makes it possible for everyone involved in any transaction to see what happened, when, and who performed it (both parties). For example: In an industry where supply chains are often complex and lengthy (e-commerce), blockchain helps simplify the process by providing a secure way for vendors and manufacturers to record each transaction concerning each other so that tracking and tracing become much more accessible.
The purpose of blockchain is to enable decentralized trust. Satoshi Nakamoto first proposed the blockchain in 2008, but it was only with the invention of Bitcoin that it became popular. The purpose of blockchain is to create a shared public ledger of all transactions in the network. This is done by creating blocks that are chained together in order. When a new block is created, it contains information about the previous block and data about the transaction that needs to be recorded.
The beauty of this system is that it keeps track of all transactions without having to trust any other entity. The data cannot be altered because it is distributed across a network of computers and stored in multiple locations. Each computer connected to the network has its copy of the ledger, so if one computer were hacked, another could still validate the transaction history. Blockchain is a new way of keeping track of information and ensuring that it’s secure, but it’s not just for banks. It’s being used across industries to help improve efficiency, reduce fraud and make life easier for businesses of all sizes. Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that records and verifies transactions between two parties in a secure, encrypted, and verifiable manner. The process also allows tracking assets from one owner to another without third-party approval.
Blockchain is a distributed ledger that records and stores continuous data (blocks) in chronological order. In other words, information stored on the blockchain is immutable and cannot be corrupted. This feature makes blockchain valuable for many purposes, like storing sensitive data, verifying ownership, or issuing new currency or shares to investors.
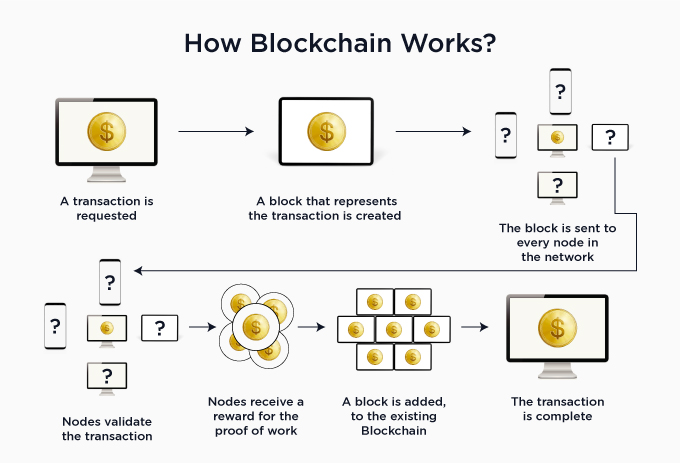
Blockchain has no single point of failure, which means if one party stops supporting the blockchain, many other parties can continue verifying its integrity. The distributed nature of the blockchain makes it practically impossible for any organization or individual to tamper with it without being detected. Moreover, since all participants in the network participate in verifying transactions, there is no need for third parties, such as governments or banks, to play a central role in verifying transactions or keeping records on them. This makes blockchain highly secure and robust compared to traditional methods used today by financial institutions such as banks.
The blockchain is a shared, immutable, and decentralized database that contains records of all transactions. The people who run the computers that generate the blockchain are called “miners.” Each miner in the Bitcoin network is responsible for adding a block to the blockchain, a list of all previous blocks. Since each new block contains all of the information from all previous blocks, it becomes a continuously growing list of records.
Each transaction on the Bitcoin network must be recorded and verified for it to be added to the blockchain. For example, when you purchase with Bitcoin at an online retailer, your payment will be sent across the network to be processed by one of those computers that are part of the bitcoin network’s decentralized structure. After it receives your payment and verifies what you’re paying for (the product or service), it adds it to its copy of the blockchain, as well as any other transactions that have occurred since your last purchase was recorded on its composition of the blockchain.
Blockchain is a technology that enables peer-to-peer transactions without the need for an intermediary. It is a distributed ledger that uses cryptography to ensure data integrity and authenticity.
In simple terms, blockchain is a decentralized database that maintains records of transactions between parties. The transactions are permanent and cannot be altered or deleted once they are recorded on the distributed ledger. Blockchain technology is a decentralized ledger that stores data, executes transactions, and transmits value. This technology has numerous benefits, including:
Blockchain is a transparent and open-source system that provides a secure and reliable platform for companies to share information. Using blockchain technology, users can access the same data from any location without the risk of being hacked or having their information compromised. Blockchain technology provides transparency for all parties involved in the transaction, which helps to minimize fraud and ensure that money goes where it’s intended to go when it’s supposed to go there and that no one has tampered with it.
Blockchain technology makes it possible for anyone with access to the Internet to see how much money they have in their account at any given time. This allows users to easily control their finances and make changes as needed without going through an intermediary such as a bank or credit card company.
The security of blockchain technology is based on cryptography, which uses complex codes to encrypt network communications and store data. The coding system prevents hackers from accessing or changing data in any way. Blockchain technology ensures that no single entity controls your data or access to your account. Instead, all data is stored on multiple nodes across a decentralized network run by participants who contribute resources like processing power or storage space in exchange for digital currency (e.g., Bitcoin).
Digital wallets allow users to store personal information securely on their own devices rather than by a third party, reducing the risk of identity theft and giving users more control over their data. Distributed databases eliminate data duplication and increase accuracy because no single entity controls all records, improving data integrity for businesses and consumers.
Blockchain technology offers an affordable solution for businesses that need to improve efficiency and reduce costs by eliminating expensive intermediaries such as banks or other financial institutions. This allows companies to save money by bypassing traditional banking processes altogether.
Reducing the time it takes to process transactions can reduce costs because fewer employees are needed, and more periodic systems need to be maintained. In addition, using blockchain reduces errors because it eliminates the need for human error when making updates or changes.
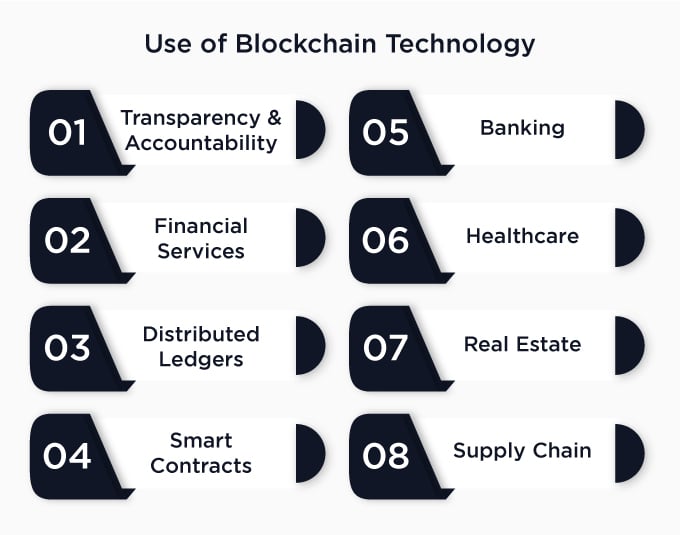
Blockchain is the technology that powers cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. A distributed ledger system records all transactions, called blocks, linked and secured by complex cryptography. A blockchain is a powerful tool for financial services companies because it can help them verify their customers’ identities and prevent fraud. For example, banks can use blockchain to ensure that each customer has a unique account number and that their identity has not been duplicated or stolen. Blockchain is a revolutionary technology that has the potential to transform many industries. Here are some of its most exciting applications:
Blockchain is a decentralized ledger that records transactions by assigning a unique digital signature to each participant. This makes it impossible for any single party to tamper with the data. The fact that each transaction is stored on multiple computers worldwide ensures that all copies are accurate, transparent, and available at all times. This allows blockchain-based systems to provide unprecedented transparency and accountability compared with traditional systems, which often rely on human oversight and fallible human judgment.
People who want to trade financial assets (such as stocks or bonds) can now use blockchain technology to record ownership accurately and securely. This improves the accuracy of transactions, reduces fraud, cuts costs, and increases efficiency in the trading process. For example, stock exchanges are currently grappling with how they can increase liquidity while reducing settlement times from days to seconds or even milliseconds through biometrics such as facial recognition technology or voice recognition software.
This means that transactions are stored on multiple nodes in a network and updated simultaneously by consensus. These distributed ledger networks can track events, contracts, and more. Verified Ledger Technology (VLT) allows organizations to record transactions without relying on third-party auditors or intermediaries. This can help reduce fraud and make processes more efficient. Blockchain technology can also create private networks between two or more entities that share information in real time instead of through traditional means like email or phone calls. This can be used for sharing medical records, supply chain management, and even data sharing among hospitals and clinics.
Smart contracts run on blockchains and are self-executing contracts that execute automatically when certain conditions are met — such as payment of funds through escrow mechanisms. They require no central authority to operate, making them ideal for smart cities where autonomous vehicles must perform certain tasks at a specific time or in response to specific events. These are self-executing contracts that use blockchain technology to execute when certain conditions are met automatically. For example, if you buy a house with bitcoin, the seller will receive their payment immediately and automatically. This eliminates the need for escrow services like escrow agents or title insurers who hold onto the funds until both parties have signed off on the transaction.
Blockchain technology can reduce costs and increase efficiency, making banking more affordable for consumers. Banks can use blockchain to process transactions, conduct audits and improve security. Bank-to-bank transfers are experiencing high transaction costs due to the lack of standardization across different financial institutions. With blockchain, banks could save millions of dollars annually by eliminating unnecessary intermediaries and charging lower service fees. Banks could also automate specific tasks, such as batch reconciliation between branches or countries.
Blockchain can help healthcare providers reduce costs, improve patient privacy and enhance data integrity by improving how they store access and share information. Blockchain also has the potential to reduce fraud, improve supply chain visibility, increase transparency and make it easier for patients to manage their health records. Blockchain has the potential to transform healthcare as well, but it will take some time and investment before we see widespread implementation in this industry. Patient records can be encrypted and stored in a decentralized fashion instead of on one centralized server; this reduces security risks and makes it difficult for hackers to access sensitive information stored on those servers.
Real estate developers are already experimenting with blockchain solutions to streamline property transactions by eliminating the need for paperwork and paper-based processes. Blockchain could also track assets across multiple properties through smart contracts that automatically transfer titles when conditions are met. The technology can record and validate property title ownership, resulting in secure and transparently recorded ownership. It also allows for cross-border transactions, which are currently challenging to complete due to legal issues between countries.
Blockchain has the potential to disrupt supply chains by allowing companies to track products as they move through the system. This means that companies can identify counterfeit products or fraud much faster than they could before, which could dramatically improve their ability to protect themselves against these types of attacks. With blockchain, each item can be tracked from its origin through production, distribution, and retail sales. As an added benefit, it’s easier for manufacturers to keep track of their inventories and monitor production processes because it’s all recorded on one ledger system.
Blockchain is a distributed ledger that serves as the foundation of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin. Blockchain technology is a reasonably new concept. It’s the basis for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but it can be used for much more than just money. It also powers other applications, including the digital currency Ethereum, which can be used to launch decentralized apps. Blockchain has become one of the most widely used technologies .in technology today because it solves many problems that other technologies have failed to address effectively.
© 2025 by Speed1 INC.